Back to General Dermatology
What is Rosacea?
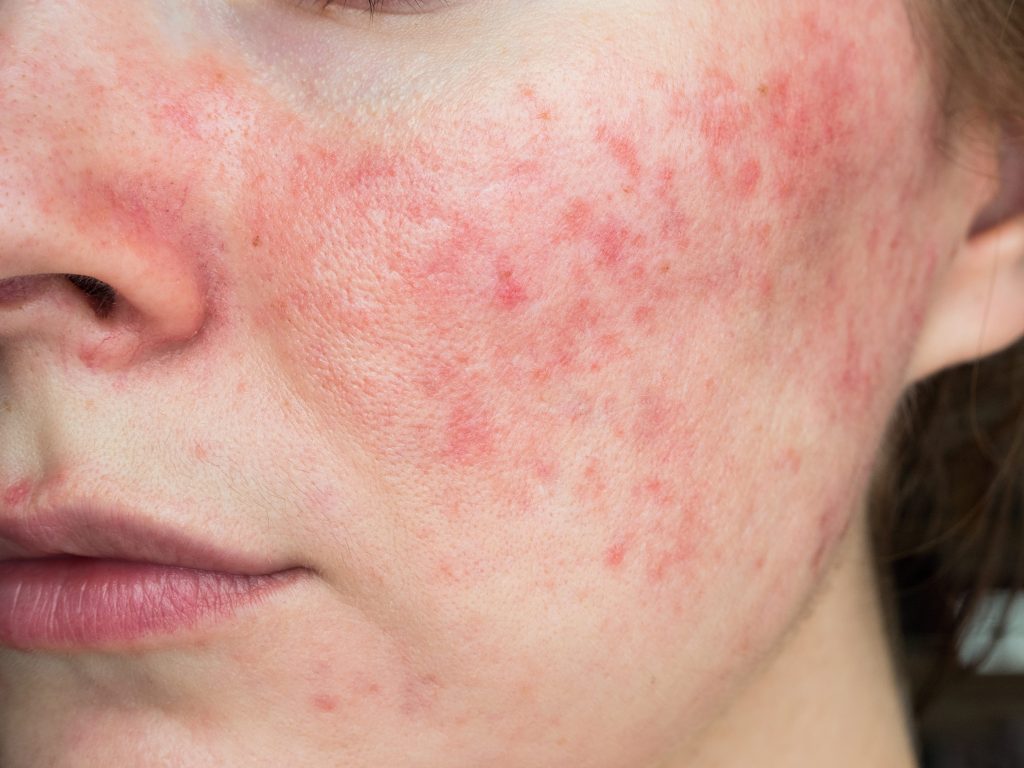
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects the face, leading to redness, flushing, the appearance of small blood vessels, and pimply breakouts. It commonly occurs in adults between the ages of 30 and 50 and is more prevalent in individuals with fair skin. While the exact cause of rosacea is unknown, factors such as genetics, abnormal blood vessel responses, microorganisms and an overactive immune system are believed to play a role.
Symptoms of Rosacea
- Flushing and blushing: Spontaneous and recurrent episodes of flushing or blushing. Common triggers of flushing include caffeine, heat, wind or cold, alcohol (especially red wine), spicy food, emotions and stress.
- Facial redness and prominent blood vessels: Overtime, frequent flushing leads to persistent facial redness. Redness tends to localize to the central face, including the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. Small, visible blood vessels (telangiectasia) may appear.
- Acne-like bumps: Papulopustular rosacea may also be characterized by small, red, pus-filled bumps resembling acne. In rosacea, these breakouts tend to localize to the midface.
- Eye symptoms: Approximately half of individuals with rosacea experience eye symptoms such as dryness, irritation, and inflammation of the eyelids (blepharitis).
- Rhinophyma: Rhinophyma is a thickening and deformity of the nose secondary to proliferation of the sebaceous glands in the skin. This is an uncommon finding in rosacea that is seen in men. The onset occurs most commonly between age 40-60.
Triggers and Lifestyle Factors
- Sun exposure: Prolonged sun exposure or extreme temperatures can trigger or worsen rosacea symptoms.
- Certain foods and beverages: Spicy foods, hot beverages, alcohol, and certain food additives have been reported to trigger rosacea flare-ups.
- Emotional factors: Stress, anxiety, and emotional factors can contribute to rosacea flare-ups.
- Skincare and cosmetic products: Harsh skincare products, fragrances, and certain cosmetic ingredients can irritate the skin and worsen rosacea symptoms.
- Other triggers: Exercise, hot baths, saunas, and exposure to wind or cold weather can trigger rosacea symptoms in some individuals.
Treatment Options for Rosacea
- Topical medications: Prescription creams or gels containing ingredients such as metronidazole, ivermectin, azelaic acid, tacrolimus or brimonidine can help reduce redness and inflammation associated with rosacea.
- Oral medications: In more severe cases, oral antibiotics, such as tetracycline or doxycycline, may be prescribed to control inflammation and reduce symptoms.
- Laser and light therapies: Pulsed dye laser (PDL), KTP, or intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy, can effectively target visible blood vessels and reduce redness. They can also be effective at decreasing pimply eruptions.
- Skincare adjustments: Gentle skincare routines using mild, non-irritating products are essential for managing rosacea. Sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF) should be worn daily.
- Lifestyle modifications: Identifying and avoiding triggers, managing stress, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the frequency and severity of rosacea flare-ups.
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that requires long-term management. While there is no cure, understanding the triggers and implementing appropriate treatment measures can significantly reduce the impact of rosacea on your skin and improve quality of life. If you suspect you have rosacea or need guidance on treatment options, please call to schedule an appointment with one of our highly skilled board-certified medical providers who can help you.
