Back to General Dermatology
What are Warts?
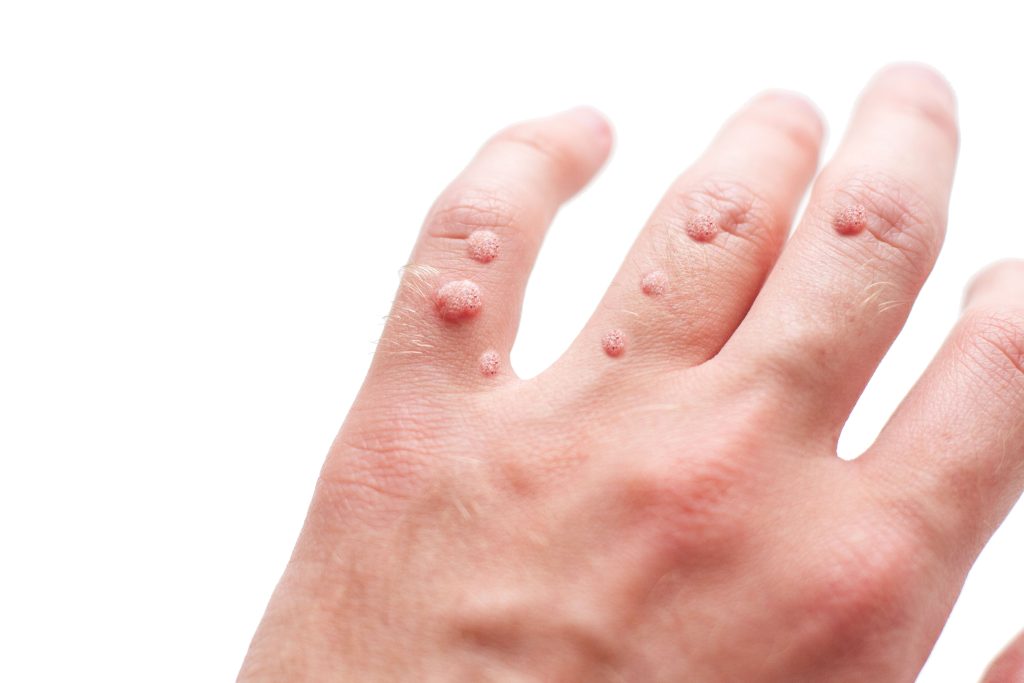
Warts are benign skin growths caused by the HPV virus. They can develop on any part of the body, including the hands, feet, face, or genital area. Warts can have multiple morphologies ranging from small flat topped bumps to rougher bumps with black dots in them. They are contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or by touching surfaces that have come into contact with the virus.
Types of Warts
- Common Warts (Verruca Vulgaris): Common warts usually appear on the hands, fingers, or around the nails. They have a rough, raised surface and may contain black dots, which are small thrombosed blood vessels.
- Plantar Warts: Plantar warts develop on the soles of the feet and can be quite painful, especially when walking or standing. They often have a thick, callus-like appearance with tiny black dots.
- Flat Warts: Flat warts are small, smooth, and flat-topped bumps. They can appear in clusters, usually on the face, neck, hands, or legs. They can spread quickly in areas of shaving.
- Genital Warts: Genital warts are sexually transmitted and affect the genital area. They can appear as small, flesh-colored bumps or have a cauliflower-like appearance. Genital warts require specialized medical attention.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Warts are caused by various strains of HPV. Different types of HPV are responsible for different types of warts.
- Direct Contact: Warts can spread through direct contact with an infected person or by touching surfaces that have been contaminated with the virus.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with a weakened immune system, such as those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, are more susceptible to developing warts.
Treatment Options for Warts
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments: Various OTC treatments, such as salicylic acid-based solutions, gels, or patches, can be applied directly to the wart to help dissolve it over time. Duct tape can also be applied to warts.
- Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen, causing it to blister and eventually fall off.
- Electrosurgery: In electrosurgery, the wart is burned off using an electric current.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatment uses focused light to destroy the vasculature of the wart tissue to disrupt the blood supply to the wart.
- Surgical Removal: Surgical excision may be necessary for larger or stubborn warts that do not respond to other treatments.
- Immunotherapy: In some cases, stimulating the immune system with medications like imiquimod may be effective in treating warts.
- Oral Cimetidine: Oral cimetidine has also been shown to treat warts in patients who have recalcitrant or more widespread warts.
Prevention and Self-Care
- Avoiding Direct Contact: To prevent the spread of warts, avoid direct contact with infected individuals or surfaces.
- Keep Skin Clean and Dry: Maintaining good hygiene and keeping the skin clean and dry can help prevent warts from developing.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share personal items such as towels, razors, or shoes, as they may contribute to the spread of warts.
Warts can be bothersome and affect both physical appearance and comfort. However, effective treatment options are available to help you remove warts and prevent their spread. If you have warts, please call to schedule an appointment with one of our highly skilled board-certified medical providers for personalized treatment options and advice.
